🌕🌕🌗 336. 回文对
2022年10月10日
- algorithm
🌕🌕🌗 336. 回文对
难度: 🌕🌕🌗
问题描述
解法 1 - 借助前缀树
class Solution {
Node root;
public List<List<Integer>> palindromePairs(String[] words) {
// 思路:
// 最先想到的是 暴搜,两层遍历,找到满足条件的回文串,复杂度 O(N * N * M)
// 优化:
// 若 x & y 可以形成回文串
// len1 == len2 时,x & y 互为逆序
// len1 > len2 时,x 可以拆分为 x1 & x2,此时满足条件 x1 & y 互为逆序 & x2 自身为回文串
// len1 < len2 时,y 可以拆分为 y1 & y2,此时满足条件 y & y2 互为逆序 & y1 自身为回文串
// 所以现在要做的就是,将所有元素添加到一个数据结构中
// 然后遍历所有元素,将 cur 拆分为 [0, j] & [j, len - 1] 两部分
// 若 [0, j] 为回文串,判断数据结构中是否存在 [j + 1, len - 1] 的逆序, 可以与之形成回文串,进而组成 完整的大回文串
// 若 [j, len - 1] 为回文串,判断数据结构中是否存在 [0, j - 1] 的逆序,可以与之形成回文串
// 由于单词只由 26 个小写字母组成,因此可以采用 前缀树 存储
// 由于单词集合中单词均不重复,因此可以使用基本数据类型记录单词的下标
root = new Node(-1); // 虚拟根节点
// 初始化前缀树
int total = words.length;
for(int i = 0; i < total; i ++) {
insert(words[i], i);
}
// 遍历所有元素
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < total; i ++) {
String str = words[i]; // 当前字符串,从前缀树中找到满足条件的匹配字串
int len = str.length();
// 查找 len1 == len2 的情况
int tmpIndex = find(str, 0, len - 1);
if(tmpIndex != -1 && tmpIndex != i) {
List<Integer> tmpList = new ArrayList<>();
tmpList.add(i);
tmpList.add(tmpIndex);
res.add(tmpList);
}
// 前串 & 后串 必含有 str 的一个字符
for(int j = 0; j < len; j ++) {
if(isStr(str, 0, j)) {
// [0, j] 为回文串,查找 前缀树中是否存在 [j + 1, len - 1] 的逆序
int index = find(str, j + 1, len - 1);
if(index != i && index != -1) { // 与之能形成回文串的字串不能是自身,必须是 2 个不同下标处的单词
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(index);
list.add(i);
res.add(list);
}
}
if(isStr(str, j, len - 1)) {
// [j, len - 1] 为回文串,查找 [0, j - 1] 的逆序
int index = find(str, 0, j - 1);
if(index != -1 && index != i) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(i);
list.add(index);
res.add(list);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 向前缀树中插入节点
private void insert(String str, int index) {
Node cur = root;
int len = str.length();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
int tmpIndex = str.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(cur.child[tmpIndex] == null) {
cur.child[tmpIndex] = new Node(-1);
}
cur = cur.child[tmpIndex];
}
cur.end = true; // 标记终止位
cur.val = index; // 其实这里 index 只要 != -1 就能说明是终止节点,end 状态位发挥的作用重复,也可以不要该标志位
}
// 到前缀树中查找 [left, right] 的逆序子串是否存在
private int find(String str, int left, int right) {
if(right >= str.length() || left < 0) {
return -1;
}
Node cur = root;
// 从高位开始往低位遍历
for(int i = right; i >= left; i --) {
int tmpIndex = str.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(cur.child[tmpIndex] == null) {
return -1; // 不存在
}
cur = cur.child[tmpIndex];
}
return cur.val;
}
private boolean isStr(String str, int left, int right) {
while(left < right) {
if(str.charAt(left) != str.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left ++;
right --;
}
return true;
}
}
// 前缀树节点类
class Node {
int val; // 值为 数组中元素下标
boolean end; // 判断是否为终点,既然是查找某个单词的逆序,那么必须终止在叶子节点
Node[] child;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.child = new Node[26];
}
}
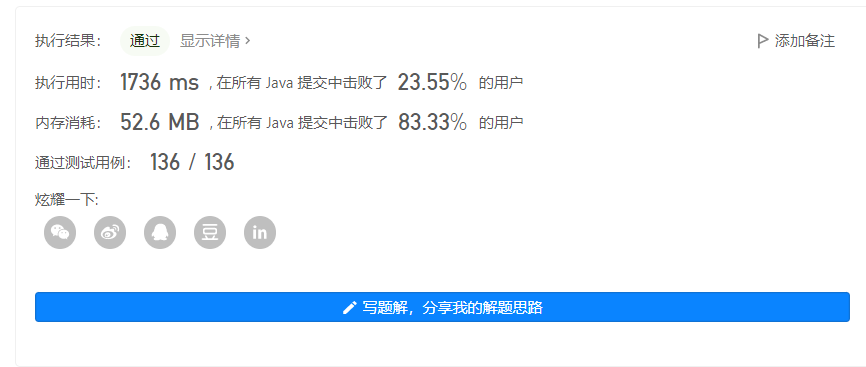
输出 1
解法 2 - 借助 HashMap
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> palindromePairs(String[] words) {
// 思路:
// 不采用字典树记录字符串的倒序,而是借助 HashMap<String, Integer> 记录
// 复杂度 O(N * M * M) - 某个单词的 前缀 & 后缀 分别为 M 复杂度
int len = words.length;
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 初始化 map
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
// 表示 某个下标处的单词的逆序
map.put(new StringBuilder(words[i]).reverse().toString(), i);
}
// 遍历所有元素
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
String str = words[i];
int size = str.length();
// 单独判断是否存在 某个单词 的逆序 ~? 为当前单词
// 若存在,说明 str & ? 可以形成回文串
if(map.containsKey(str)) {
int index = map.get(str);
if(index != i) {
addRes(res, i, index);
}
}
// 截取的字串至少含有一个字符
for(int j = 0; j < size; j ++) {
if(isStr(str, 0, j)) {
// [0, j] 为回文串,[?] + [0, j] + [j + 1, len - 1]
String iwant = str.substring(j + 1, size);
// System.out.println(str + " : " + iwant + " " + iwant.length());
if(map.containsKey(iwant)) {
int index = map.get(iwant);
if(index != i) {
addRes(res, index, i);
}
}
}
if(isStr(str, j, size - 1)) {
// [j, len - 1] 为回文串,[0, j - 1] + [j, len - 1] + [?]
String iwant = str.substring(0, j);
if(map.containsKey(iwant)) {
int index = map.get(iwant);
if(index != i) {
addRes(res, i, index);
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void addRes(List<List<Integer>> res, int i, int j) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(i);
list.add(j);
res.add(list);
}
private boolean isStr(String str, int left, int right) {
while(left < right) {
if(str.charAt(left) != str.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left ++;
right --;
}
return true;
}
}
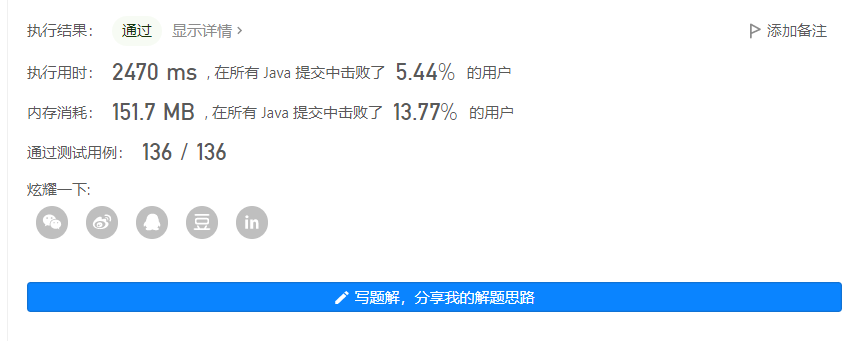
输出