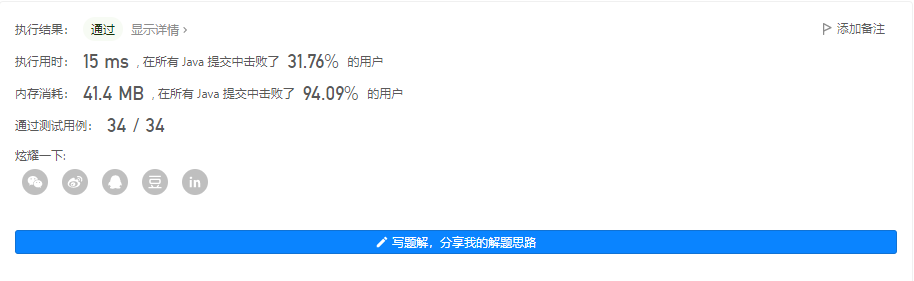
🌕🌕🌕 126. 单词接龙 II
2022年10月10日
- algorithm
🌕🌕🌕 126. 单词接龙 II
难度: 🌕🌕🌕
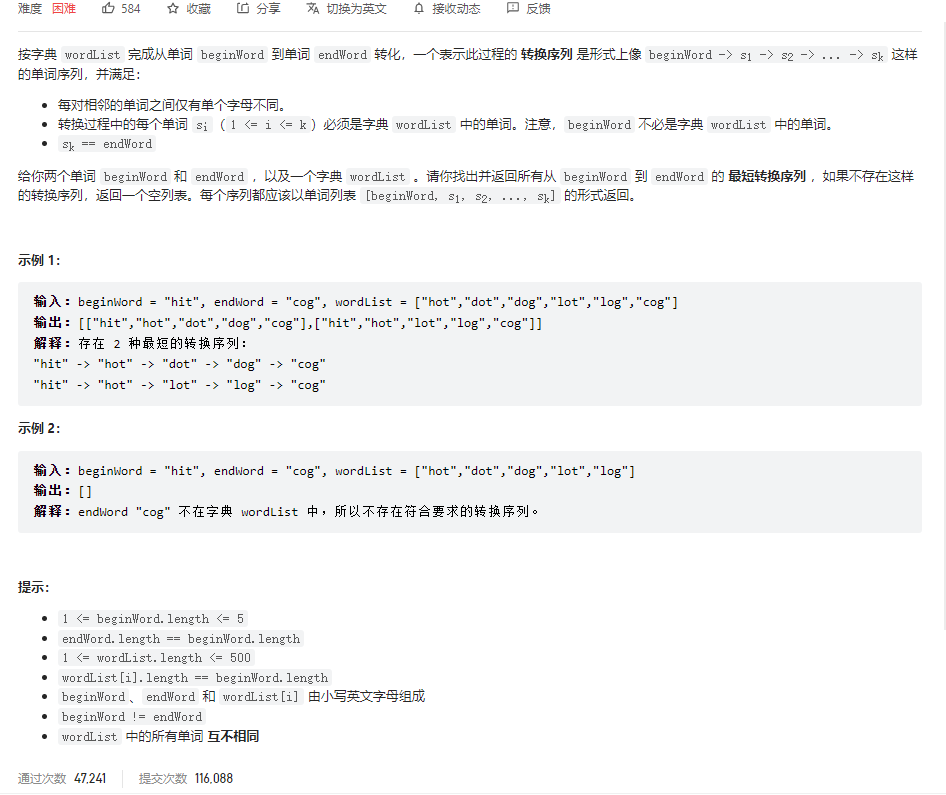
问题描述
解法
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res;
public List<List<String>> findLadders(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
// 思路:
// 图的遍历 - 同时用到了广搜 & 深搜
// 广搜 - 双向遍历,每次扩展边数少的一边,判断是否存在转换序列,并把每个节点的下一级可以连接节点结果保存
// 深搜 - 求路径
res = new ArrayList<>();
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>(wordList);
if(!set.contains(endWord)) {
return res;
}
// 把起始节点添加进集合
set.add(beginWord);
HashMap<String, HashSet<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
int count = bfs(beginWord, endWord, set, map);
// printMap(map);
// System.out.println(count);
if(count < 0) {
return res; // 说明不存在任何一条转换序列
}
// 存在,进行深搜,找到所有路径
LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList<>();
path.addLast(beginWord);
mySol(endWord, map, count, beginWord, path);
return res;
}
private void mySol(String endWord,
HashMap<String, HashSet<String>> map,
int count,
String pre,
LinkedList<String> path) {
// 递归终止条件
if(path.size() == count) {
if(pre.equals(endWord)) {
res.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
}
return;
}
HashSet<String> set = map.get(pre);
if(set != null) {
for(String next : set) {
path.addLast(next);
mySol(endWord, map, count, next, path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
private int bfs(String beginWord, String endWord, HashSet<String> wordList, HashMap<String, HashSet<String>> map) {
boolean found = false;
int total = wordList.size();
// 创建 辅助队列 & 集合
LinkedList<String> headQ = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<String> headS = new HashSet<>();
LinkedList<String> tailQ = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<String> tailS = new HashSet<>();
// 添加头尾节点
headQ.offer(beginWord);
headS.add(beginWord);
tailQ.offer(endWord);
tailS.add(endWord);
// flag 标志,判断当前是头部遍历 还是 尾部遍历
boolean flag = true;
int count = 2; // 起始就已经有 2 个节点
// 节点路径
LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList<>();
path.addFirst(beginWord);
path.addLast(endWord);
while(!headQ.isEmpty() && !tailQ.isEmpty()) {
// 双方均没有走到无法继续进行的地步
if(headQ.size() > tailQ.size()) {
// 需要切换头尾队列
flag = !flag;
LinkedList<String> tmpQ = headQ;
headQ = tailQ;
tailQ = tmpQ;
HashSet<String> tmpS = headS;
headS = tailS;
tailS = tmpS;
}
// 保证每次都从头部开始广搜,通过 flag 判断当前的头部到底是初始的头部还是尾部
// 既然需要往下走,那么节点数 ++
count ++;
int len = headQ.size();
// 依次取出当前可以走的路径,判断是否可以和尾部已有的节点重合,如果有,说明当前是最短路径
// 遍历当前下所有路径,把能够成功的所有路径添加到 res,返回
// 若不存在,当前路径压入队列,继续广搜
HashSet<String> nextSet = new HashSet<>(); // 当前层 next 节点单独存放
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
String cur = headQ.poll();
// 寻找 cur 可以到达的 next 节点
for(String next : wordList) {
if(headS.contains(next)) {
// 这一步找了好久的问题,
// 可能出现同一层前面节点没有满足条件,直接将其 next 节点加入的情况
// 因此需要将同一层的 next 节点统一添加到一个新的 set 中去
// 如果直接全部加入 nextSet 会超时,因此采用 headS 添加的同时,加入到 nextS
if(!nextSet.contains(next)) {
continue; // 当前方向已经遍历过该节点,说明不是本轮其他节点的下一个节点
}
}
if(!isValid(cur, next)) {
continue; // next 不是与 cur 匹配的 next
}
// 找到符合条件的 next 节点
// 判断是否可以和尾端匹配
if(tailS.contains(next)) {
// 更改标志位,表示已经找到满足条件的节点,下一轮就不需要了,但是当前轮还是需要继续进行
if(!found) {
found = true;
count --; // 说明是首个匹配的转换序列
}
} else {
if(!nextSet.contains(next)) { // 这里也是优化的点,保证不超时
nextSet.add(next);
headS.add(next);
headQ.offer(next);
}
}
// System.out.println(cur + " " + next + " " + flag);
// printSet(headS);
// 当前没有找到任何满足条件的转换序列,填充 map
if(flag) {
// 说明是正向遍历,from == cur
if(!map.containsKey(cur)) {
HashSet<String> tmpS = new HashSet<>();
tmpS.add(next);
map.put(cur, tmpS);
} else {
HashSet<String> tmpS = map.get(cur);
tmpS.add(next);
map.put(cur, tmpS);
}
} else {
// 反向遍历,from == next,因为之后深搜需要按照正向方向进行
if(!map.containsKey(next)) {
HashSet<String> tmpS = new HashSet<>();
tmpS.add(cur);
map.put(next, tmpS);
} else {
HashSet<String> tmpS = map.get(next);
tmpS.add(cur);
map.put(next, tmpS);
}
}
}
}
if(found) {
return count;
}
}
return -1; // 说明没有一条转换序列
}
private boolean isValid(String a, String b) {
int len = a.length();
int diff = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
if(a.charAt(i) != b.charAt(i)) {
if(diff == 1) {
return false;
} else {
diff ++;
}
}
}
return diff == 1;
}
private void printMap(HashMap<String, HashSet<String>> map) {
for(Map.Entry<String, HashSet<String>> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("key: " + entry.getKey());
System.out.print("value: ");
for(String cur : entry.getValue()) {
System.out.print(cur + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
}
}
private void printSet(HashSet<String> set) {
for(String cur : set) {
System.out.print(cur + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
}
}
输出