🌕🌕 224. 基本计算器
2022年10月10日
- algorithm
🌕🌕 224. 基本计算器
难度: 🌕🌕
问题描述
解法
class Solution {
public int calculate(String s) {
// 思路:
// 双栈 - 一个栈存放值,一个栈存放运算符
// 由于运算符只有 +/- ()
// 因此优先级就是遇到 右括号 则计算括号内的运算,直到遇到左括号,括号里面肯定是 +/- 优先级同级
int len = s.length();
LinkedList<Integer> valS = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Character> singS = new LinkedList<>();
int index = 0;
if(s.charAt(0) == '-') {
valS.push(0); // 防止出现 -2 + 1 这种数字栈不够的情况
}
while(index < len) {
char c = s.charAt(index);
if(getSingleNumber(c) >= 0) {
// 数字直接压栈
int[] tmpArr = getNumber(s, len, index);
int num = tmpArr[0];
index = tmpArr[1];
valS.push(num);
// System.out.println(index);
} else if(c == ' ') {
index ++;
continue; // 空格继续
} else if(c == '(') {
// 左括号直接压栈
singS.push(c);
index ++;
} else if(c == '+' || c == '-') {
// 符号位压栈前,计算能计算的部分,防止出现 2 - 1 + 1 变成了 1 + 1 - 2 的情况
while(!singS.isEmpty() && singS.peek() != '(') {
char sign = singS.pop();
int b = valS.pop();
int a = valS.pop();
if(sign == '+') {
valS.push(a + b);
} else {
valS.push(a - b);
}
}
singS.push(c); // 符号位压栈
if(index > 0 && s.charAt(index - 1) == '(' && c == '-') {
// 即 左括号 后面紧跟了 负号
valS.push(0);
}
index ++;
} else {
// 右括号 - 弹栈
while(singS.peek() != '(') {
char sign = singS.pop();
int b = valS.pop();
int a = valS.pop();
if(sign == '+') {
valS.push(a + b);
} else if(sign == '-') {
valS.push(a - b);
}
}
singS.pop(); // 弹出与之对应的左括号
index ++;
}
}
// 判断 符号栈 中是否还有符号 - 剩下的肯定都是 +/-
while(!singS.isEmpty()) {
char sign = singS.pop();
int b = valS.pop();
int a = valS.pop();
if(sign == '+') {
valS.push(a + b);
} else if(sign == '-') {
valS.push(a - b);
}
}
return valS.peek();
}
private int[] getNumber(String s, int len, int left) {
int res = -1;
int i = left;
for(; i < len; i ++) {
int cur = getSingleNumber(s.charAt(i));
if(cur >= 0) {
if(res == -1) {
res = cur;
} else {
res = res * 10 + cur;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
return new int[]{res, i};
}
private int getSingleNumber(char c) {
if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
return c - '0';
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
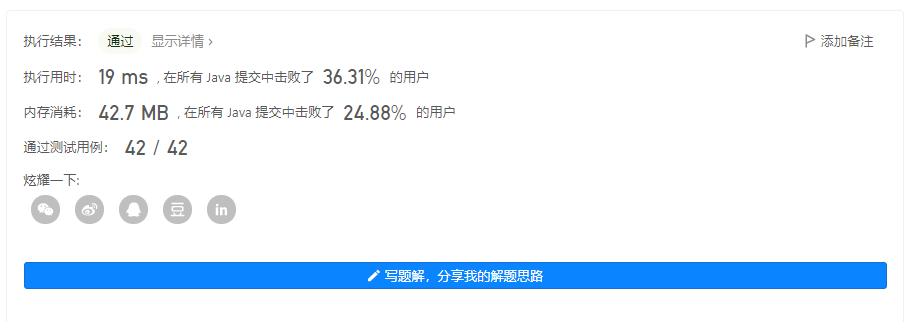
输出
解法 2 - 进阶[四则计算器含括号]
class Solution {
public int calculate(String s) {
// 思路:
// 双栈 - 一个栈存放值,一个栈存放运算符
// 运算符含 +/- */ ()
// 空格 - 继续
// 数字 - 直接压数字栈
// 左括号 - 直接压符号栈
// 右括号 - 依次计算括号内的值,结果压数字栈
// +-*/ - 在压栈前先将能运算的部分运算出来,即比较优先级,同级 | 低级的可以运算,然后压栈
// 特别:
// 当出现 初始为 负号 | 括号内初始为 负号 的情况,需要先压 0 入数字栈
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 保存不同运算符的优先级
map.put('+', 1);
map.put('-', 1);
map.put('*', 2);
map.put('/', 2);
map.put('(', 3);
map.put(')', 3);
int len = s.length();
LinkedList<Integer> valS = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Character> singS = new LinkedList<>();
int index = 0;
if(s.charAt(0) == '-') {
valS.push(0); // 防止出现 -2 + 1 这种数字栈不够的情况
}
while(index < len) {
char c = s.charAt(index);
if(getSingleNumber(c) >= 0) {
// 1. 数字直接压栈
int[] tmpArr = getNumber(s, len, index);
int num = tmpArr[0];
index = tmpArr[1];
valS.push(num);
// System.out.println(index);
} else if(c == ' ') {
// 2. 空格继续
index ++;
continue; // 空格继续
} else if(c == '(') {
// 3. 左括号直接压栈
singS.push(c);
index ++;
} else if(c == '+' || c == '-') {
// 符号位压栈前,先计算能计算的部分,即同级 | 高优先级的部分
while(!singS.isEmpty() && map.get(c) <= map.get(singS.peek())) {
cal(singS, valS);
}
singS.push(c); // 符号位压栈
if(index > 0 && s.charAt(index - 1) == '(' && c == '-') {
// 即 左括号 后面紧跟了 负号
valS.push(0);
}
index ++;
} else {
// 右括号 - 弹栈
while(singS.peek() != '(') {
cal(singS, valS);
}
singS.pop(); // 弹出与之对应的左括号
index ++;
}
}
// 判断 符号栈 中是否还有符号 - 剩下的肯定都是 +/-
while(!singS.isEmpty()) {
char sign = singS.pop();
int b = valS.pop();
int a = valS.pop();
if(sign == '+') {
valS.push(a + b);
} else if(sign == '-') {
valS.push(a - b);
}
}
return valS.peek();
}
private void cal(LinkedList<Character> singS, LinkedList<Integer> valS) {
char sign = singS.pop();
int b = valS.pop();
int a = valS.pop();
if(sign == '+') {
valS.push(a + b);
} else if(sign == '-') {
valS.push(a - b);
} else if(sign == '*') {
valS.push(a * b);
} else if(sign == '/') {
valS.push(a / b);
}
}
private int[] getNumber(String s, int len, int left) {
int res = -1;
int i = left;
for(; i < len; i ++) {
int cur = getSingleNumber(s.charAt(i));
if(cur >= 0) {
if(res == -1) {
res = cur;
} else {
res = res * 10 + cur;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
return new int[]{res, i};
}
private int getSingleNumber(char c) {
if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
return c - '0';
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
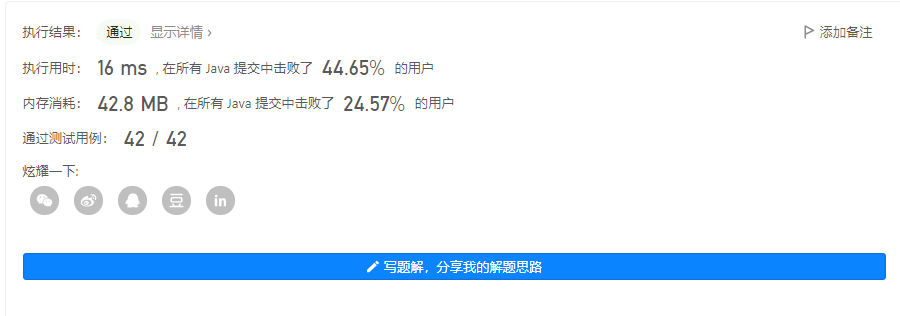
输出 2