🏀 TreeMap
2022年6月9日
- Java
🏀 TreeMap
1. 类注释
- 概述
TreeMap是基于NavigableMap类实现的红黑树- 根据默认自然顺序排序或者根据构造函数中指定的排序器进行排序
- 复杂度
- O(log N):
containsKeygetputremove
非线程安全
Iterator 是 fail-fast 的
R-B 树 特点
- 每个节点都有颜色,
R|B - 根节点 =
B - 叶子节点不存数据 =
B- 这里的叶子节点包括 空节点
- 当前节点 ==
R则父 & 子节点 ==B - 任意节点到叶子节点的所有路径经过的
B数相同
2. 类图
public class TreeMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
// ......
}
3. 属性
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
/**
* The number of entries in the tree
*/
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* The number of structural modifications to the tree.
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
4. 构造函数
/**
* 添加默认构造器,key 必须实现 Comparable 接口,且是 comparable 的,更不可抛出 ClassCastExp
* 例如将一个 String 类型的 key 加入到一堆 Integer 类型中,则会抛出上述异常
*/
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
/**
* 指定构造器的构造函数
*/
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
/**
* 有参构造函数,根据 map 的 comparator 依次插入所有元素
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws ClassCastException if the keys in m are not {@link Comparable},
* or are not mutually comparable
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
/**
* 将 map 中所有元素插入到 本 treemap 中
*
* @param map mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of a key or value in
* the specified map prevents it from being stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null or
* the specified map contains a null key and this map does not
* permit null keys
*/
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {
int mapSize = map.size();
if (size==0 && mapSize!=0 && map instanceof SortedMap) { // 有序集合,沿用有序集合自身 comparator
Comparator<?> c = ((SortedMap<?,?>)map).comparator();
if (c == comparator || (c != null && c.equals(comparator))) {
++modCount;
try { // 若 map 为有序 map,根据 有序集合建树
buildFromSorted(mapSize, map.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
return;
}
}
super.putAll(map); // 使用默认 comparator
}
/**
* 有参构造函数,根据 有序集合 的 comparator 依次插入所有元素
*
* @param m the sorted map whose mappings are to be placed in this map,
* and whose comparator is to be used to sort this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
/**
* 根据 有序数据 线性时间复杂度 建树
*
* @param size - Iterator | Stream 中 K-V 对的 数量
* @param it - 从 Iterator 中读取 K-V 建树
* @param str - 若非空,则新节点从 Stream 中读取建树
* @param defaultVal - 若非空,建树时,所有 key 对应 val 均应为 defaultVal;若为空,建树时 key 对应的 val 为 Iterator 的值
* @throws java.io.IOException propagated from stream reads. This cannot
* occur if str is null.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException propagated from readObject.
* This cannot occur if str is null.
*/
private void buildFromSorted(int size, Iterator<?> it,
java.io.ObjectInputStream str,
V defaultVal)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
this.size = size;
root = buildFromSorted(0, 0, size-1, computeRedLevel(size), it, str, defaultVal);
}
/**
* 递归的“辅助方法”,它完成了前一种方法的实际工作。相同命名的参数具有相同的定义。下面记录了其他参数。
* 假设在调用此方法之前已经设置了 TreeMap 的比较器和大小字段。 (它忽略这两个字段。)
*
* @param level - 树的当前高度,初始时应该为 0
* @param lo - 子树首节点的下标,初始时应为 0
* @param hi - 子树末尾节点的下标,初始时应为 size-1
* @param redLevel - 红节点应该处于的层数,应该等于 根据当前数量的节点数的红黑树的计算高度
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private final Entry<K,V> buildFromSorted(int level,
int lo,
int hi,
int redLevel,
Iterator<?> it,
java.io.ObjectInputStream str,
V defaultVal)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
/*
* 策略:根是最中间的元素。为了得到它,我们必须首先递归地构造整个左子树,以便抓取它的所有元素。然后我们可以继续右子树。
*
* lo 和 hi 参数是从当前子树的迭代器或流中提取的最小和最大索引。它们实际上并没有被索引,我们只是按顺序进行,确保以相应的顺序提取项目。
*/
if (hi < lo)
return null;
int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
Entry<K,V> left = null;
if (lo < mid) // 说明至少 3 个节点,左子树非空 - 递归建左树
left = buildFromSorted(level+1, lo, mid - 1, redLevel, it, str, defaultVal);
// 从 Iterator | Stream 中读取 K-V
K key;
V value;
if (it != null) { // 优先从 Iterator 读取
if (defaultVal==null) {
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>)it.next();
key = (K)entry.getKey();
value = (V)entry.getValue();
} else {
key = (K)it.next();
value = defaultVal;
}
} else { // 从 Stream 读取
key = (K) str.readObject();
value = (defaultVal != null ? defaultVal : (V) str.readObject());
}
Entry<K,V> middle = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
// 非完整最底层红色的颜色节点
if (level == redLevel)
middle.color = RED;
if (left != null) {
middle.left = left;
left.parent = middle;
}
if (mid < hi) { // 递归建 右树
Entry<K,V> right = buildFromSorted(level+1, mid+1, hi, redLevel, it, str, defaultVal);
middle.right = right;
right.parent = middle;
}
return middle;
}
/**
* 找到将所有节点分配到黑色的级别。这是 buildTree 生成的完整二叉树的最后一个“完整”级别。其余节点为红色。
* (这使得未来插入的颜色分配“很好”。)这个级别数是通过找到到达第零节点所需的分割数来计算的。
* (答案是~lg(N),但在任何情况下都必须通过相同的快速 O(lg(N)) 循环来计算。)
*/
private static int computeRedLevel(int sz) {
int level = 0;
for (int m = sz - 1; m >= 0; m = m / 2 - 1)
level++;
return level;
}
5. 内部节点类
// Red-black mechanics
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
/**
* 树中的节点。兼作将键值对传递回用户的一种方式(参见 Map.Entry)。
*/
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
/**
* 默认构造函数,节点色为黑色
*/
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue());
}
public int hashCode() {
int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode());
int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
return keyHash ^ valueHash;
}
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
6. 常用方法
1. get(Object key)
/**
* 返回 key 对应的 val 或 null
* 若返回的是 null 并不意味着不存在这个 key,也可能是这个 key 对应的 val 本身为 null
* 可通过 containsKey 函数进行区分
*
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
/**
* 返回此映射的给定键条目,如果映射不包含该键的条目,则返回 {@code null}。
*
* @return this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map
* does not contain an entry for the key
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // 说明 TreeMap 的 key 不能为空
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
// 二叉树的查找 - 基于默认构造器
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 返回 key 所对应的 Entry<K, V>
* 若不存在该 key 则返回最接近于 key 但是比 key 要大的 Entry<K, V>
* 若也不存在,则返回 null
* 等同于 getHigherEntry(K key)
*/
final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
// key < cur 往左子树继续找
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
// key > cur 往右子树找
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
} else {
// 右子树 == null 往父节点找
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
// 当前节点为左子节点,则父节点即目标节点;若当前节点为右节点,那么值 > 父节点,因此还需要继续往上找
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else
return p;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 返回 key 所对应的 Entry<K, V>
* 若不存在该 key 则返回最接近于 key 但是比 key 要小的 Entry<K, V>
* 若也不存在,则返回 null
* 等同于 getLowerEntry(K key)
*/
final Entry<K,V> getFloorEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else
return p;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 返回 最接近 key 值但 比 key 大的节点,若不存在,返回 null
*/
final Entry<K,V> getHigherEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else {
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 返回 最接近 key 值但 比 key 小的节点,若不存在,返回 null
*/
final Entry<K,V> getLowerEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else {
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}
2. put(K key, V value)
/**
* 添加元素
* 若使用默认排序器,则 key 非空
* 若该 key 已存在,则覆盖旧值
* 返回 旧值 | null
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
*
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
// 树当前为 null,新增节点即为 root
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); // 默认颜色为 B
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
// 树非空 - 定位到要插入的节点位置
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
} else {
// 使用默认排序器
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // 说明红黑树中 key 不能为 空
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t; // t == root 从 根节点开始查找,确定插入位置
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value); // 该 key 已经存在,直接修改节点值,然后返回
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e); // 插入节点后重新维护 红黑树
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
/** From CLR */
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
// R-B 树新插入节点必须为 R 色
x.color = RED;
// x != root 说明 x 肯定有 parent 节点 & parent != null 但 parent 可能 == root
// x.parent.color == RED 说明 父子节点均为 R,需要进行调整
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
// 当前节点的父节点 == 当前节点的爷爷的左儿子 == 当前节点的左叔
// 即,父亲 == 左叔
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
// y == 右叔
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
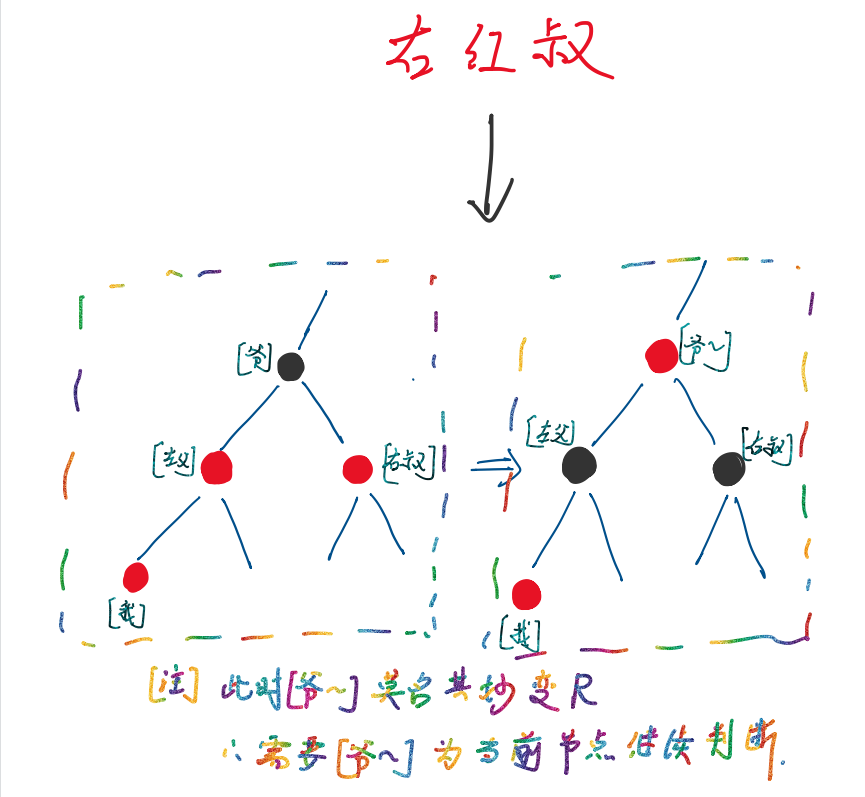
// 右红叔 则 右叔必变色,因为不管怎么调整,总有一个节点会变成红色,到右叔本来的位置
// 这样就出现了父子均红的情况
// 右红叔 只变色,该轮不旋转,只调整我的位置
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 父[左叔] 变黑
setColor(y, BLACK); // 右叔 变黑
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 爷爷变红
x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); // x == 爷爷
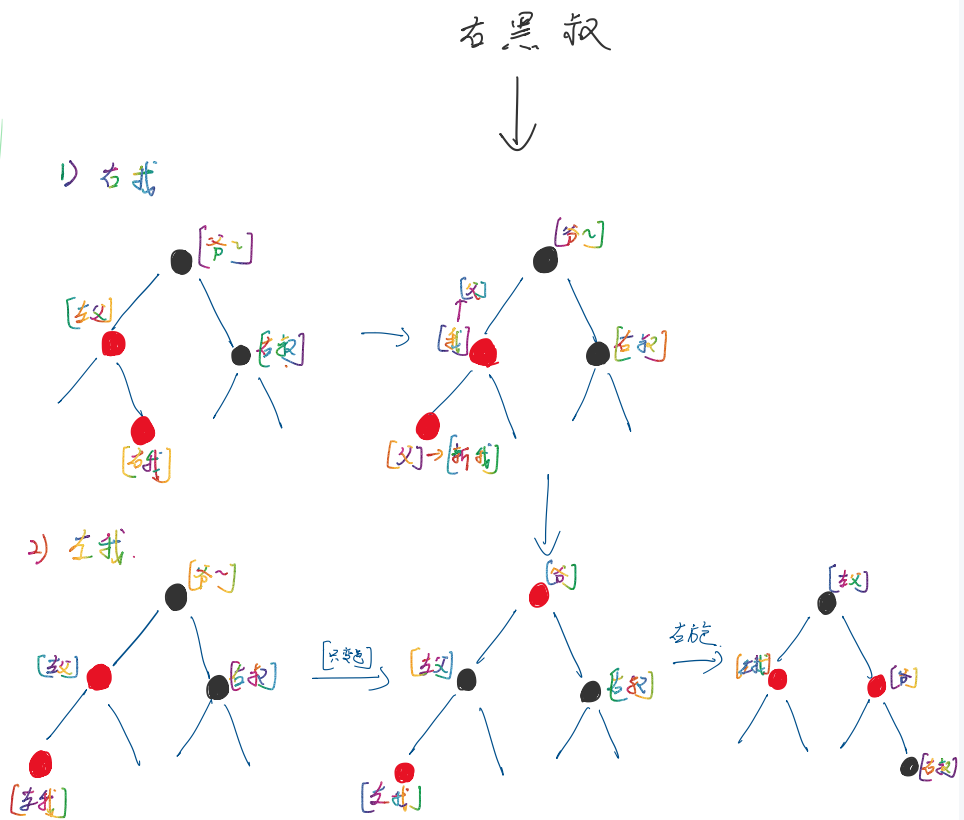
} else {
// 右叔 = 黑,可以看成 右叔 = Null
// 右叔不需要变色
// 我为右我,则需要调整 我和父 的位置,将父左旋,我为父
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
// 无论本身是左我,还是父左旋后,我均为左我
// 此时,需要将爷爷右旋调整平衡,同时变色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 父变黑,将成为新的爷爷
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 爷爷变 R,将成为右黑叔
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); // 将爷爷右旋
}
} else {
// 父 == 右叔
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); // y == 左叔
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
// 左红叔需要变色,类似于 父 == 左叔 && 右红叔
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 父变黑
setColor(y, BLACK); // 左红叔变黑
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 爷爷变红
x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); // x == 爷爷
} else {
// 我 == 左我,需要将父右旋
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
// 我 == 右我,此时变色 + 将爷爷左旋
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
root.color = BLACK; // 插入节点始终确保根节点为黑
}
/** From CLR */
// 只左旋,不变色
// p 的右节点将成为新的 p,而 p 将成为 左节点
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> r = p.right;
p.right = r.left;
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
r.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
else
p.parent.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
}
/** From CLR */
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> l = p.left;
p.left = l.right;
if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
l.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = l;
else if (p.parent.right == p)
p.parent.right = l;
else p.parent.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
}
3. remove(Object key)
/**
* Removes the mapping for this key from this TreeMap if present.
*
* @param key key for which mapping should be removed
* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared
* with the keys currently in the map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null keys
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree.
*/
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// 找到 p 的继任者 s ,两者交换位置
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
// 被替换节点有孩子
if (replacement != null) {
// 将 p 的替换者 和 p 的父亲关联,这样 p 就架空了
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// 替换要删除节点位置的源节点若为 B,则需要调整平衡
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
// 被替换节点没有孩子 & 父节点为空
// 出现这种情况的原因是,红黑树本身就一个节点,现在要删除这个唯一节点
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
// 被替换节点没有孩子,但是有父亲
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
/**
* 找到当前节点的下一个节点,也就是比它大的最接近他的节点
*/
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
/** From CLR */
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
// 当前节点 非根节点 & 为黑
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
// 为左我
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
// sib == 右我
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
// 右我为红,则 变色 + 父左旋
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
// 右我为黑
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else { // symmetric
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}