🏉 ConcurrentHashMap
2022年6月20日
- Java
🏉 ConcurrentHashMap
1. 类注释 & JDK 7
1) JDK 7
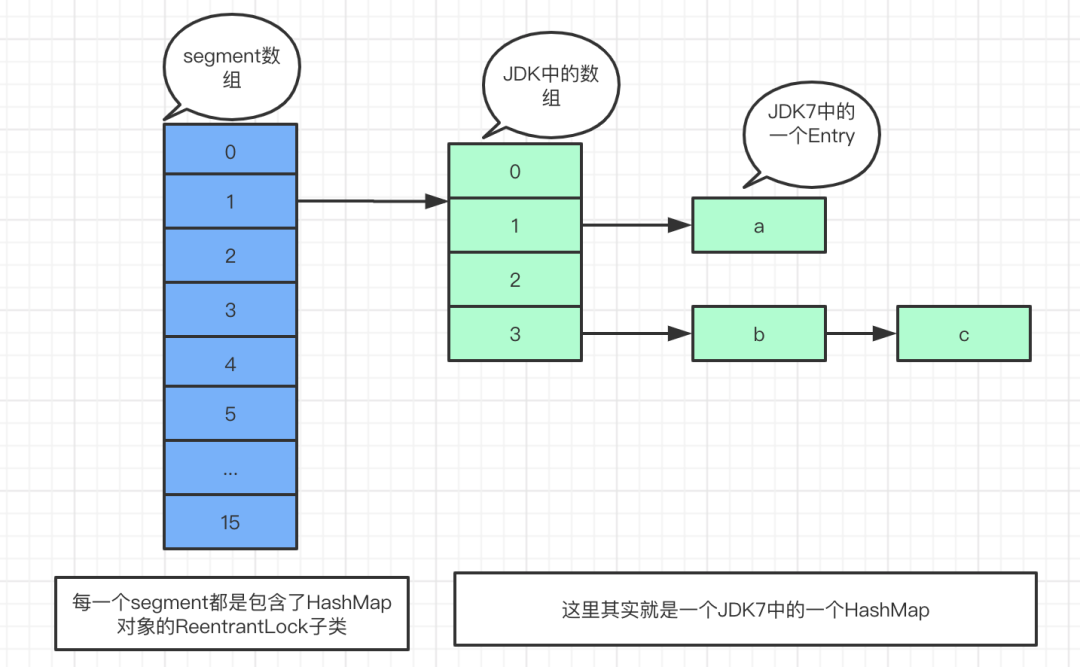
ConcurrentHashMap由Segment数组结构和HashEntry数组组成
Segment是一种可重入锁,extends ReentrantLock,类中包含一个HashEntry数组- 每个
HashEntry是一个链表结构 - 通过
Segment分段锁,ConcurrentHashMap实现了高效率的并发 - 但并发程度由
segment数组元素个数决定,并发度一旦初始化无法扩容
size()
- 该方法用来求 K-V 对元素个数
- 先无锁情况下统计每个
Segment的元素个数,求和后判断前后两次总和是否相同 - 若相同,则返回 sum
- 若不同,再重复 2 次无锁求和
- 若 3 次计算均无法满足要求,则将所有
Segment加锁lock(),再求和
2) 类注释
key&val均非空,类似于HashTableget()操作不会发生阻塞,支持并发,没有锁机制 &CAS方法size()isEmpty()containsValue()只在没有其他线程对其进行更新操作时正确,否则结果只反映了瞬态的值,可以用于监测 | 估算,但不足以进行程序控制
补充
- 采用了 数组 + 链表 + 红黑树 的数据结构
- 并发时,并发度最大为 数组容量大小
- 采用 CAS + synchronized 进行并发控制
CAS主要用于put()操作时,对应数组下标没有任何节点- 更新
baseCount操作 transfer()操作时,当前负责下标处为空,CAS 置 fwd 表示已经迁移完成
synchronized主要用于put()操作时,锁住要插入元素所在数组下标的头结点transfer()操作时,锁住本线程负责迁移下标范围的当前下标的头结点replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv)clear()treeifyBin()
2. 类图
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable {
// ......
}
3. 属性
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246763182397L;
/* ---------------- 常量部分 -------------- */
/**
* 最大容量
* 为了保证数组分配,以及 32 位 hash 的前2位被用于 标志位
*/
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* 默认数组容量大小,必须为 2 的幂 && 最大为 MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* 数组最大长度
*/
static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* 默认并发度,并未被使用,只是为了兼容以前的版本
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
/**
* 负载因子,并未被实际使用,而是通过 n - (n >>> 2) 判断
*/
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* >= 8 时转红黑树
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* <= 6 退化为链表
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* >= 64 时才转红黑树,否则会先扩容
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
/**
* 每个线程每次协助迁移的数组下标个数最小值,必须 >= DEFAULT_CAPACITY
*/
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
/**
* 用于 sizeCtl 的位数,对于 32 位数组来说,必须 >= 6,sizeCtl 代表的值见下
*/
private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
/**
* 最多有多少条线程可以同时协助扩容
*/
private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1;
/**
* 一个 32 位 int,分为 2 部分,一部分记录有多少条线程在协助扩容;一部分记录每个线程负责扩容过程中的节点迁移个数
*/
private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;
/*
* Encodings for Node hash fields. See above for explanation.
*/
static final int MOVED = -1; // 正在扩容
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // 已经转换成树
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // 获得hash值的辅助参数
/** 获取可用的 CPU 个数 */
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/** For serialization compatibility. */
private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields = {
new ObjectStreamField("segments", Segment[].class),
new ObjectStreamField("segmentMask", Integer.TYPE),
new ObjectStreamField("segmentShift", Integer.TYPE)
};
/* ---------------- 字段 -------------- */
/**
* 数组,只有初次插入时才进行初始化,长度为 2 的幂
*/
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* 用于扩容,只有在扩容时才非空
*/
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
/**
* 记录元素个数,当无竞争时才有效,通过 CAS 进行更新
*/
private transient volatile long baseCount;
/**
* 控制数组的初始化 & 扩容操作
* 当 < 0 时,表示数组正在初始化 | 扩容
* -1 表示初始化
* -n 表示正在有 (n - 1) 个线程正在进行扩容操作
* 0 表示数组还没有进行初始化
* > 0 表示元素个数达到多少时才会触发下一次的扩容
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
/**
* The next table index (plus one) to split while resizing.
*/
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
/**
* Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating CounterCells.
*/
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
/**
* Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
*/
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
// views
private transient KeySetView<K,V> keySet;
private transient ValuesView<K,V> values;
private transient EntrySetView<K,V> entrySet;
/* ---------------- 静态工具 -------------- */
/**
* 高位 & 低位异或
*/
static final int spread(int h) {
return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;
}
/**
* 基于给定值,保证返回最接近给定值的比它大的 2 的幂
*/
private static final int tableSizeFor(int c) {
int n = c - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
4. 内部类
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return val; }
public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); }
public final String toString(){ return key + "=" + val; }
public final V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
(k == key || k.equals(key)) &&
(v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));
}
/**
* Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.
*/
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
Node<K,V> e = this;
if (k != null) {
do {
K ek;
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
return null;
}
}
5. 构造函数
/**
* 1. 什么也不做
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
/**
* 2. 根据指定 initialCapacity 确定 sizeCtl,这里的 sizeCtl 在 initTable() 时会作为初始数组的长度
* sizeCtl >= (1.5initialCapacity + 1)
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// sizeCtl 扩容阈值 >= (1.5initialCapacity + 1)
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1)); // >= 1.5 + 1 初始容量的 2 的幂
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
/**
* 3. 创建一个带有指定初始容量、加载因子和默认 concurrencyLevel (1) 的新的空映射
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
/**
* 4. 创建一个带有指定初始容量、加载因子和并发级别的新的空映射
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
/**
* 5. 将 给定 map 转换为 ConcurrentHashMap
*
* @param m the map
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
tryPresize(m.size());
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
putVal(e.getKey(), e.getValue(), false);
}
/**
* Tries to presize table to accommodate the given number of elements.
*
* @param size number of elements (doesn't need to be perfectly accurate)
*/
private final void tryPresize(int size) {
int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1);
int sc;
while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table;
int n;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) { // 原数组为空
n = (sc > c) ? sc : c;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { // 当前线程 CAS 尝试初始化数组
try {
if (table == tab) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
}
} else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
break;
else if (tab == table) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
Node<K,V>[] nt;
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the stamp bits for resizing a table of size n.
* Must be negative when shifted left by RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT.
*/
static final int resizeStamp(int n) {
return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1));
}
6. 常用方法
1) get(Object key)
/**
* 返回 key 对应的 value | null
* 支持多线程并发,不加锁,用到了 tabAt() 函数保证每次取到的都是最新值
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table;
int n = tab.length;
Node<K,V> e, p;
int n, eh;
K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
// 表不为空并且表的长度大于0并且key所在的桶不为空
if (tab != null && n > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
// 表中的元素的hash值与key的hash值相等
eh = e.hash; // 获取头节点的 hash 值
if (eh == h) {
// 说明只能是头节点
ek = e.key;
if (ek == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
} else if (eh < 0) { // 说明是该节点下是红黑树,进行红黑树的查找
p = e.find(h, key); // e 作为头节点,判断是否存在 Hash == h && Key == key 的节点
return p != null ? p.val : null; // 是个TreeBin hash = -2
}
// 不是红黑树,进行链表的查找
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
/*
* 使用了 unSafe 方法
* 通过直接操作内存的方式来保证并发处理的安全性,使用的是硬件的安全机制
* table[i] 数据是通过 Unsafe 对象通过 反射 获取的
* 在java内存模型中,每个线程都有一个工作内存,里面存储着table的「副本」,
* 虽然table是 volatile 修饰的,但不能保证里面的每个元素均为最新值
* Unsafe.getObjectVolatile 可以直接获取指定内存的数据,「保证了每次拿到数据都是最新的」
*/
// 用来返回节点数组的指定位置的节点的原子操作
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U;
private static final long SIZECTL;
private static final long TRANSFERINDEX;
private static final long BASECOUNT;
private static final long CELLSBUSY;
private static final long CELLVALUE;
private static final long ABASE;
private static final int ASHIFT;
static {
try {
U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = ConcurrentHashMap.class;
SIZECTL = U.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("sizeCtl"));
TRANSFERINDEX = U.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("transferIndex"));
BASECOUNT = U.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("baseCount"));
CELLSBUSY = U.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("cellsBusy"));
Class<?> ck = CounterCell.class;
CELLVALUE = U.objectFieldOffset(ck.getDeclaredField("value"));
Class<?> ak = Node[].class;
ABASE = U.arrayBaseOffset(ak);
int scale = U.arrayIndexScale(ak);
if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0)
throw new Error("data type scale not a power of two");
ASHIFT = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
2) put(K key, V value)
/**
* Key & Val 均非空
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// key & val 均非空
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 求 根据 key 得到的 hash
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f;
int n, i, fh;
// 数组为空,进行初始化
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
// 对应插入位置为空,此时 CAS 插入元素
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // CAS 插入成功,跳出循环。失败了重新进入该 for 循环
} else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); // 正在扩容,需要协助扩容
else {
// 数组有了,下标处头结点也有了,现在也不是扩容中,因此正常遍历该下标处的节点,进行插入操作
V oldVal = null;
// 锁住该下标处的头结点
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) { // 说明是链表
binCount = 1; // 记录链表长度
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val; // 在原链表中找到原有节点,判断是否进行原值覆盖
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
// 之前没有该节点,尾插法插入元素
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
break;
}
}
} else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { // 说明是红黑树
Node<K,V> p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value));
binCount = 2;
if (p != null) { // 已经存在该节点
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value; // 需要覆盖原值
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i); // 转红黑树
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
/**
* 初始化数组
*/
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table;
int sc;
while (tab == null || tab.length == 0) {
sc = sizeCtl;
if (sc < 0)
Thread.yield(); // 已经有其他线程在进行初始化了,该线程等待
// 没有其他线程进行初始化操作,本线程通过 CAS 尝试将 SIZECTL 变为 -1
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
// 变更成功,说明本线程获得初始化数组的资格
try {
tab = table;
if (tab == null || tab.length == 0) { // 再次判断
// 1) 无参构造函数时,sc == 0 --> 初始数组长度 == 16
// 2) 只指定容量时,sc == tableSizeFor(1.5initialCapacity + 1)
// 3) 指定 初始容量 & 负载因子 & 并发级别时,sc == tableSizeFor(1 + initialCap/loadFactor)
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2); // 0.75n 表示新的下一次扩容阈值
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
/**
* 协助扩容
*/
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab;
int sc;
// table不是空 且 node节点是转移类型,并且转移类型的 nextTable 不是空 说明还在扩容ing
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
// 确定新table指向没有变,老table数据也没变,并且此时 sizeCtl小于0 还在扩容ing
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab && (sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
// 1. 生成的标识符改变
// 2. 扩容结束 【疑问?】
// 3. 达到最大可以协助扩容的线程数
// 4. 扩容转移下标已经 <= 0 说明不需要协助了
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
// sc ++ 表示现在又多了一个线程协助扩容
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
transfer(tab, nextTab); // 进行原数组元素转移到新数组
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
/**
* 再扩容阶段需要用到的节点类
* hash == -1
* 放在数组下标的头结点处
* 若看到该节点,则表明该节点已经完成迁移操作,不需要管
*/
static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
super(MOVED, null, null, null); // 该节点类的 hash == MOVED == -1
this.nextTable = tab;
}
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
// loop to avoid arbitrarily deep recursion on forwarding nodes
outer: for (Node<K,V>[] tab = nextTable;;) {
Node<K,V> e; int n;
if (k == null || tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) == null)
return null;
for (;;) {
int eh; K ek;
if ((eh = e.hash) == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
if (eh < 0) {
if (e instanceof ForwardingNode) {
tab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)e).nextTable;
continue outer;
}
else
return e.find(h, k);
}
if ((e = e.next) == null)
return null;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 根据扩容中的长度为 n 的数组生成一个标识符,左移后必须为负值
* Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) : 返回无符号整型 n 的最高非零位前面的 0 的个数
*/
static final int resizeStamp(int n) {
return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1));
}
/**
* 将元素迁移到新数组中
*/
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length;
// 获取每个线程负责迁移的下标个数,与 CPU 数有关,且 >= MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE(16)
int stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n;
if (stride < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
// 判断新数组是否为 null,若是,则先进行新数组的初始化操作,扩容为原来的 2 倍
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n; // 初始开始迁移的对应原数组的尾节点下标为 n,从后往前一个线程负责一部分下标处的迁移工作
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f;
int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false; // 不需要获取负责迁移的数组下标,退出
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false; // 别的线程已经迁移完成,不需要本线程协助了,退出
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this,
TRANSFERINDEX,
nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ? nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
// 获取当前线程需要负责迁移的原数组下标范围 [transferIndex - stride, transferIndex]
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false; // 成功获取到本线程要负责迁移的数组下标范围,退出
}
}
// 已经没有还未分配的需要迁移的下标了
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
// 全部迁移完成
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab; // table 成为新数组,原新数组清空,留待下次迁移操作
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1); // 扩容阈值为新数组长度的 0.75
return;
}
// 全部迁移完成,但是 finish 标志位还未被设置,说明虽然下标已经分配给线程,
// 但有的线程还在执行自己负责的下标迁移操作
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return; // 当前线程不是最后一个还在扩容的线程,不能设置 finish 标志位,直接返回
finishing = advance = true; // 是最后一个还在扩容的线程,设置 finish 标志位,表示迁移操作全部线程均已完成
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
} else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd); // 负责迁移的该下标为 null,CAS 设置为 fwd 节点,表示该节点已完成迁移工作
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // 在负责之前就已经是完成状态,则跳过当前下标
else {
// 加锁,锁住该下标处的头结点,开始该下标处节点的迁移工作
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n; // 判断迁移后的下标是 index,还是 index + n
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
// 分成 2 条链表,分别放在新数组对应的下标处
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash;
K pk = p.key;
V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { // 红黑树的迁移
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* Adds to count, and if table is too small and not already
* resizing, initiates transfer. If already resizing, helps
* perform transfer if work is available. Rechecks occupancy
* after a transfer to see if another resize is already needed
* because resizings are lagging additions.
*
* @param x the count to add
* @param check if <0, don't check resize, if <= 1 only check if uncontended
*/
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells;
long b, s;
// 若桶非空,或者尝试 CAS 修改 baseCount 值失败
// 说明可能存在并发
if (as != null || !U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a;
long v;
int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended = U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
// 1. 桶为空,无并发
// 2. 随机取出一个桶发现是空的
// 3. 修改随机出来的桶的桶容量,发现失败
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount(); // 统计所有桶中的元素总数
}
// check >= 0 需要检查是否需要进行扩容操作
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt;
int n, sc;
// 当前元素总数 > 容量阈值 && 数组非空 && 数组长度为超范 ==> 需要进行扩容操作
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl)
&& (tab = table) != null
&& (n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
// 此时已经正在进行扩容
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break; // 当前线程不需要协助扩容
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt); // 参与扩容
} else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null); // 当前未进行扩容,需要开始扩容
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
/**
* A padded cell for distributing counts. Adapted from LongAdder
* and Striped64. See their internal docs for explanation.
*/
@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {
volatile long value;
CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
}
// See LongAdder version for explanation
// 分桶计数
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
CounterCell[] as; CounterCell a; int n; long v;
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs; int m, j;
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
}
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
// 遍历桶,统计每个桶的元素和
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells;
CounterCell a;
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}
3) 遍历
① entrySet()
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySetView<K,V> es;
return (es = entrySet) != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySetView<K,V>(this));
}
/**
* A view of a ConcurrentHashMap as a {@link Set} of (key, value)
* entries. This class cannot be directly instantiated. See
* {@link #entrySet()}.
*/
static final class EntrySetView<K,V> extends CollectionView<K,V,Map.Entry<K,V>>
implements Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;
EntrySetView(ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map) { super(map); }
public boolean contains(Object o) {
Object k, v, r; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
(r = map.get(k)) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
(v == r || v.equals(r)));
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
Object k, v; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
map.remove(k, v));
}
/**
* @return an iterator over the entries of the backing map
*/
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] t;
int f = (t = m.table) == null ? 0 : t.length;
return new EntryIterator<K,V>(t, f, 0, f, m);
}
public boolean add(Entry<K,V> e) {
return map.putVal(e.getKey(), e.getValue(), false) == null;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends Entry<K,V>> c) {
boolean added = false;
for (Entry<K,V> e : c) {
if (add(e))
added = true;
}
return added;
}
public final int hashCode() {
int h = 0;
Node<K,V>[] t;
if ((t = map.table) != null) {
Traverser<K,V> it = new Traverser<K,V>(t, t.length, 0, t.length);
for (Node<K,V> p; (p = it.advance()) != null; ) {
h += p.hashCode();
}
}
return h;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
Set<?> c;
return ((o instanceof Set) &&
((c = (Set<?>)o) == this ||
(containsAll(c) && c.containsAll(this))));
}
public Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {
Node<K,V>[] t;
ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> m = map;
long n = m.sumCount();
int f = (t = m.table) == null ? 0 : t.length;
return new EntrySpliterator<K,V>(t, f, 0, f, n < 0L ? 0L : n, m);
}
public void forEach(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] t;
if ((t = map.table) != null) {
Traverser<K,V> it = new Traverser<K,V>(t, t.length, 0, t.length);
for (Node<K,V> p; (p = it.advance()) != null; )
action.accept(new MapEntry<K,V>(p.key, p.val, map));
}
}
}
static final class EntryIterator<K,V> extends BaseIterator<K,V> implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntryIterator(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int size, int limit, ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map) {
super(tab, index, size, limit, map);
}
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
Node<K,V> p = next;
if (p== null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
K k = p.key;
V v = p.val;
lastReturned = p;
advance(); // Iterator 前进一个节点
return new MapEntry<K,V>(k, v, map);
}
}
/**
* Base of key, value, and entry Iterators. Adds fields to
* Traverser to support iterator.remove.
*/
static class BaseIterator<K,V> extends Traverser<K,V> {
final ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map;
Node<K,V> lastReturned;
BaseIterator(Node<K,V>[] tab, int size, int index, int limit, ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map) {
super(tab, size, index, limit);
this.map = map;
advance();
}
public final boolean hasNext() { return next != null; }
public final boolean hasMoreElements() { return next != null; }
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p;
if ((p = lastReturned) == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
lastReturned = null;
map.replaceNode(p.key, null, null);
}
}
/**
* Encapsulates traversal for methods such as containsValue; also
* serves as a base class for other iterators and spliterators.
*
* Method advance visits once each still-valid node that was
* reachable upon iterator construction. It might miss some that
* were added to a bin after the bin was visited, which is OK wrt
* consistency guarantees. Maintaining this property in the face
* of possible ongoing resizes requires a fair amount of
* bookkeeping state that is difficult to optimize away amidst
* volatile accesses. Even so, traversal maintains reasonable
* throughput.
*
* Normally, iteration proceeds bin-by-bin traversing lists.
* However, if the table has been resized, then all future steps
* must traverse both the bin at the current index as well as at
* (index + baseSize); and so on for further resizings. To
* paranoically cope with potential sharing by users of iterators
* across threads, iteration terminates if a bounds checks fails
* for a table read.
*/
static class Traverser<K,V> {
Node<K,V>[] tab; // current table; updated if resized
Node<K,V> next; // the next entry to use
TableStack<K,V> stack, spare; // to save/restore on ForwardingNodes
int index; // index of bin to use next
int baseIndex; // current index of initial table
int baseLimit; // index bound for initial table
final int baseSize; // initial table size
Traverser(Node<K,V>[] tab, int size, int index, int limit) {
this.tab = tab;
this.baseSize = size;
this.baseIndex = this.index = index;
this.baseLimit = limit;
this.next = null;
}
/**
* 前进一个节点
*/
final Node<K,V> advance() {
Node<K,V> e = next; // e 前进一个节点
if (e != null)
e = e.next; // e 前进一个节点后,再次前进一个节点
for (;;) {
Node<K,V>[] t;
int i, n; // must use locals in checks
// 1. 尝试更新 next,若 next.netxt != null 说明可以直接进行 .next 返回
if (e != null)
return next = e;
// 2. .next == null 说明已经是当前下标节点的最后一个,判断是否是最后一个下标,如果是,说明后续不存在节点,返回 null
if (baseIndex >= baseLimit || (t = tab) == null ||
(n = t.length) <= (i = index) || i < 0)
return next = null;
// 3. 尝试找数组下一个非空节点,判断是否处于扩容中
if ((e = tabAt(t, i)) != null && e.hash < 0) {
// 3.1 包含当前节点已经扩容完成,更新 table 为 nextTable 找到已经扩容完成后的数组
if (e instanceof ForwardingNode) {
tab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)e).nextTable;
e = null;
pushState(t, i, n);
continue;
}
else if (e instanceof TreeBin)
e = ((TreeBin<K,V>)e).first;
else
e = null;
}
if (stack != null)
recoverState(n);
else if ((index = i + baseSize) >= n)
index = ++baseIndex; // visit upper slots if present
}
}
/**
* Saves traversal state upon encountering a forwarding node.
*/
private void pushState(Node<K,V>[] t, int i, int n) {
TableStack<K,V> s = spare; // reuse if possible
if (s != null)
spare = s.next;
else
s = new TableStack<K,V>();
s.tab = t;
s.length = n;
s.index = i;
s.next = stack;
stack = s;
}
/**
* Possibly pops traversal state.
*
* @param n length of current table
*/
private void recoverState(int n) {
TableStack<K,V> s;
int len;
while ((s = stack) != null && (index += (len = s.length)) >= n) {
n = len;
index = s.index;
tab = s.tab;
s.tab = null;
TableStack<K,V> next = s.next;
s.next = spare; // save for reuse
stack = next;
spare = s;
}
if (s == null && (index += baseSize) >= n)
index = ++baseIndex;
}
}
② keySet()
public KeySetView<K,V> keySet() {
KeySetView<K,V> ks;
return (ks = keySet) != null ? ks : (keySet = new KeySetView<K,V>(this, null));
}
③ values()
public Collection<V> values() {
ValuesView<K,V> vs;
return (vs = values) != null ? vs : (values = new ValuesView<K,V>(this));
}
7. 问题补充
1) val != null
- 依据 ConcurrentHashMap 的作者的回答进行解释:
- 在并发情况下会带来 二义性
- 详细说明:
- 不论是
HashMap还是ConcurrentHashMap,经过map.get(key)函数如果得到了null的结果 - 此时无法确定到底是 不存在该 key 还是 存在该 key 但是 key.val == null 这两种情况,因此存在 二义性
- 不论是
- 此外,作者个人认为,无论是否考虑线程安全问题,都不应该允许 null 的存在
2) key != null
- 作者不希望出现 key == null 的设计,因此在代码中出现该情况会抛出异常
3) 迭代器是 强一致性 or 弱一致性?
- 弱一致性
- 在遍历过程中,内部元素被其他线程改变
- 如果改变的部分是已经遍历过的,迭代器不会反映出来
- 若改变的部分是还没有遍历过的,迭代器会输出改变后的元素情况