🌕 1195. 交替打印字符串
2022年6月20日
- algorithm
🌕 1195. 交替打印字符串
难度: 🌕
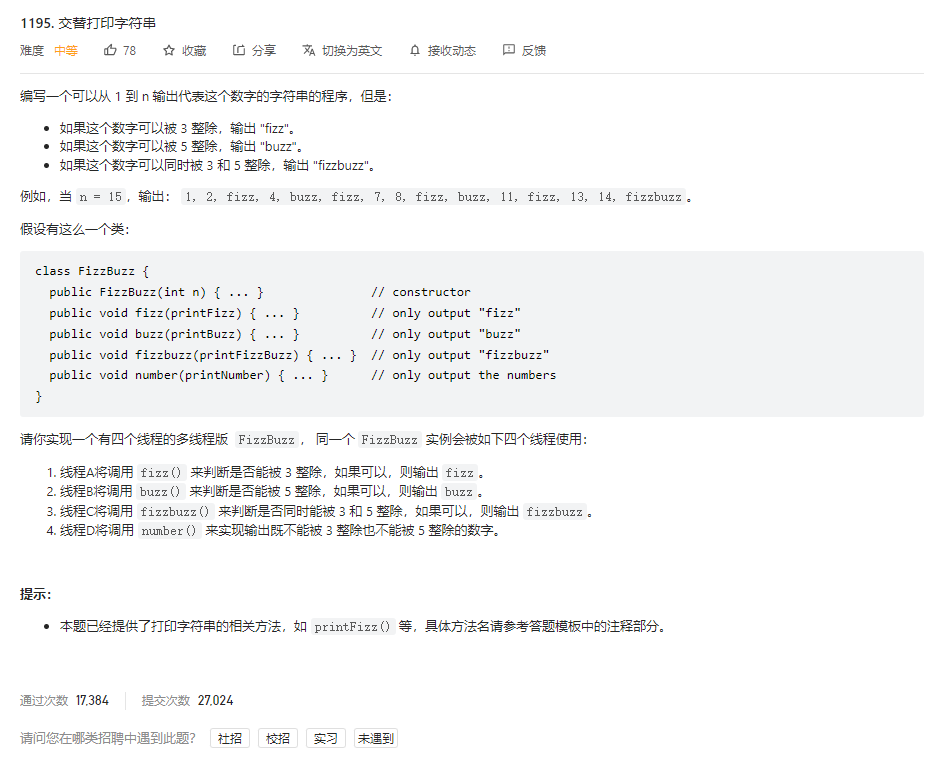
问题描述
解法1 - Semaphore
class FizzBuzz {
private int n;
Semaphore s1;
Semaphore s2;
Semaphore s3;
Semaphore s4;
private int flag;
public FizzBuzz(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.s1 = new Semaphore(0);
this.s2 = new Semaphore(0);
this.s3 = new Semaphore(0);
this.s4 = new Semaphore(1);
}
// printFizz.run() outputs "fizz".
public void fizz(Runnable printFizz) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 != 0) {
s1.acquire();
printFizz.run();
// System.out.println("fizz");
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
// printBuzz.run() outputs "buzz".
public void buzz(Runnable printBuzz) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 != 0 && i % 5 == 0) {
s2.acquire();
printBuzz.run();
// System.out.println("buzz");
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
// printFizzBuzz.run() outputs "fizzbuzz".
public void fizzbuzz(Runnable printFizzBuzz) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 == 0) {
s3.acquire();
printFizzBuzz.run();
// System.out.println("fizzbuzz");
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
// printNumber.accept(x) outputs "x", where x is an integer.
public void number(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 != 0 && i % 5 != 0) {
s4.acquire();
printNumber.accept(i);
// System.out.println(i);
// 判断接下来的数是哪种情况
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
private void mySol(int next) {
if(next % 3 == 0 && next % 5 != 0) {
s1.release();
} else if(next % 3 != 0 && next % 5 == 0) {
s2.release();
} else if(next % 3 == 0 && next % 5 == 0) {
s3.release();
} else {
s4.release();
}
}
}
解法 2 - CountDownLatch
class FizzBuzz {
// 思路:
// 这种类似的题目,只要能用 Semaphore 做,就能用 CountDownLatch 做
private int n;
CountDownLatch c1;
CountDownLatch c2;
CountDownLatch c3;
CountDownLatch c4;
private int flag;
public FizzBuzz(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.c1 = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.c2 = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.c3 = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.c4 = new CountDownLatch(0);
}
// printFizz.run() outputs "fizz".
public void fizz(Runnable printFizz) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 != 0) {
c1.await();
printFizz.run();
// System.out.println("fizz");
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
c1 = new CountDownLatch(1);
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
// printBuzz.run() outputs "buzz".
public void buzz(Runnable printBuzz) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 != 0 && i % 5 == 0) {
c2.await();
printBuzz.run();
// System.out.println("buzz");
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
c2 = new CountDownLatch(1);
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
// printFizzBuzz.run() outputs "fizzbuzz".
public void fizzbuzz(Runnable printFizzBuzz) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 == 0) {
c3.await();
printFizzBuzz.run();
// System.out.println("fizzbuzz");
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
c3 = new CountDownLatch(1);
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
// printNumber.accept(x) outputs "x", where x is an integer.
public void number(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(i % 3 != 0 && i % 5 != 0) {
c4.await();
printNumber.accept(i);
// System.out.println(i);
// 判断接下来的数是哪种情况
int next = i + 1;
if(next <= n) {
c4 = new CountDownLatch(1);
mySol(next);
}
}
}
}
private void mySol(int next) {
if(next % 3 == 0 && next % 5 != 0) {
c1.countDown();
} else if(next % 3 != 0 && next % 5 == 0) {
c2.countDown();
} else if(next % 3 == 0 && next % 5 == 0) {
c3.countDown();
} else {
c4.countDown();
}
}
}