🌕 1116. 打印零与奇偶数
2022年6月20日
- algorithm
🌕 1116. 打印零与奇偶数
难度: 🌕
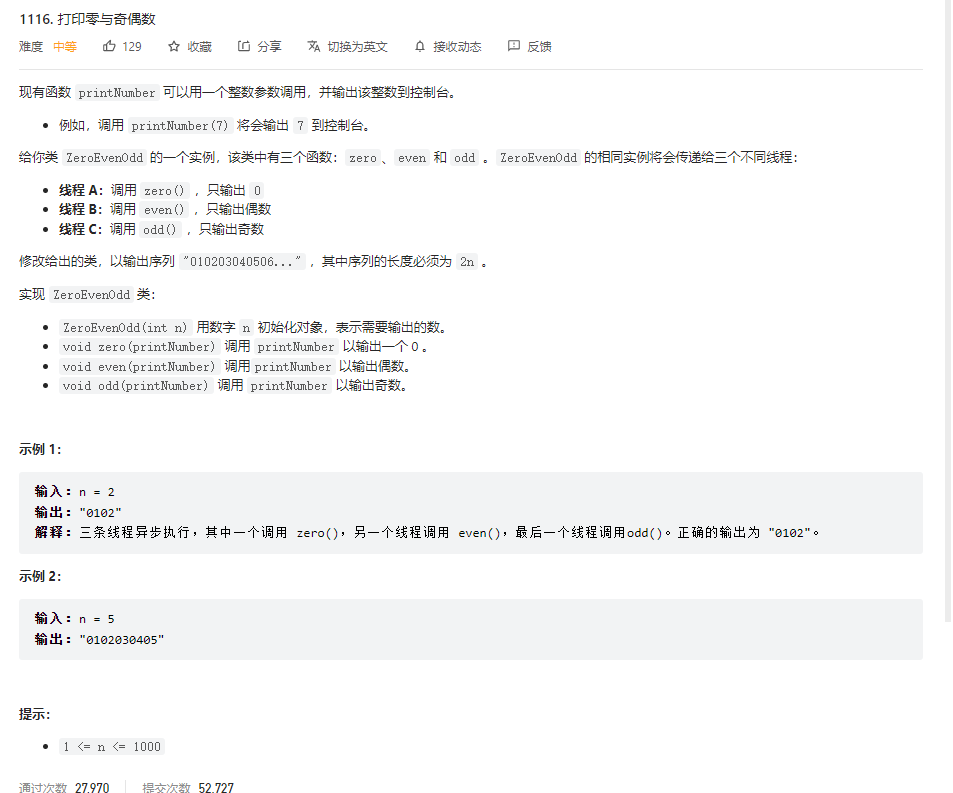
问题描述
解法 1 - ReentrantLock + Condition + flag
class ZeroEvenOdd {
// 思路:
// ReentrantLock + Condition + flag
private int n;
ReentrantLock lock;
Condition cA;
Condition cB;
Condition cC;
private boolean flagA;
private boolean flagB;
private boolean flagC;
private boolean flag; // 从 A 开始,派发给 B 还是 C
public ZeroEvenOdd(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();
this.cA = lock.newCondition();
this.cB = lock.newCondition();
this.cC = lock.newCondition();
this.flagA = true;
this.flagB = false;
this.flagC = false;
this.flag = false;
}
// printNumber.accept(x) outputs "x", where x is an integer.
public void zero(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
lock.lock();
try {
while(!flagA) {
cA.await();
}
printNumber.accept(0);
flagA = false;
this.flag = !this.flag;
if(this.flag) {
flagB = true;
cB.signal();
} else {
flagC = true;
cC.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public void odd(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2; i ++) {
lock.lock();
try {
while(!flagB) {
cB.await();
}
int cur = 2 * i + 1;
printNumber.accept(cur);
flagB = false;
flagA = true;
cA.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public void even(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i ++) {
lock.lock();
try {
while(!flagC) {
cC.await();
}
int cur = 2 * (i + 1);
printNumber.accept(cur);
flagC = false;
flagA = true;
cA.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
解法 2 - CountDownLatch
class ZeroEvenOdd {
// 思路:
// CountDownLatch
private int n;
CountDownLatch c0;
CountDownLatch c1;
CountDownLatch c2;
private int flag;
public ZeroEvenOdd(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.c0 = new CountDownLatch(0); // 一开始就启动 0
this.c1 = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.c2 = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.flag = 1;
}
// printNumber.accept(x) outputs "x", where x is an integer.
public void zero(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
c0.await();
printNumber.accept(0);
// System.out.println("zero printed");
c0 = new CountDownLatch(1); // 重新计时
if(flag == 1) {
flag = 2;
c1.countDown();
} else {
flag = 1;
c2.countDown();
}
}
}
public void odd(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2; i ++) {
c1.await();
printNumber.accept(2 * i + 1);
// System.out.println("odd printed");
c1 = new CountDownLatch(1);
c0.countDown();
}
}
public void even(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i ++) {
c2.await();
printNumber.accept(2 * (i + 1));
// System.out.println("even printed");
c2 = new CountDownLatch(1);
c0.countDown();
}
}
}
解法 3 - Semaphore
class ZeroEvenOdd {
// 思路:
// Semaphore
private int n;
Semaphore s0;
Semaphore s1;
Semaphore s2;
private int flag;
public ZeroEvenOdd(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.s0 = new Semaphore(1);
this.s1 = new Semaphore(0);
this.s2 = new Semaphore(0);
this.flag = 1;
}
// printNumber.accept(x) outputs "x", where x is an integer.
public void zero(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
s0.acquire();
printNumber.accept(0);
// System.out.println("zero printed");
if(flag == 1) {
flag = 2;
s1.release(); // 给 s1 发放一个许可
} else {
flag = 1;
s2.release();
}
}
}
public void odd(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2; i ++) {
s1.acquire();
printNumber.accept(2 * i + 1);
// System.out.println("odd printed");
s0.release();
}
}
public void even(IntConsumer printNumber) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 0; i < n / 2; i ++) {
s2.acquire();
printNumber.accept(2 * (i + 1));
// System.out.println("even printed");
s0.release();
}
}
}