🧅 JDBC 编程
2022年10月10日
- frame
🧅 JDBC 编程
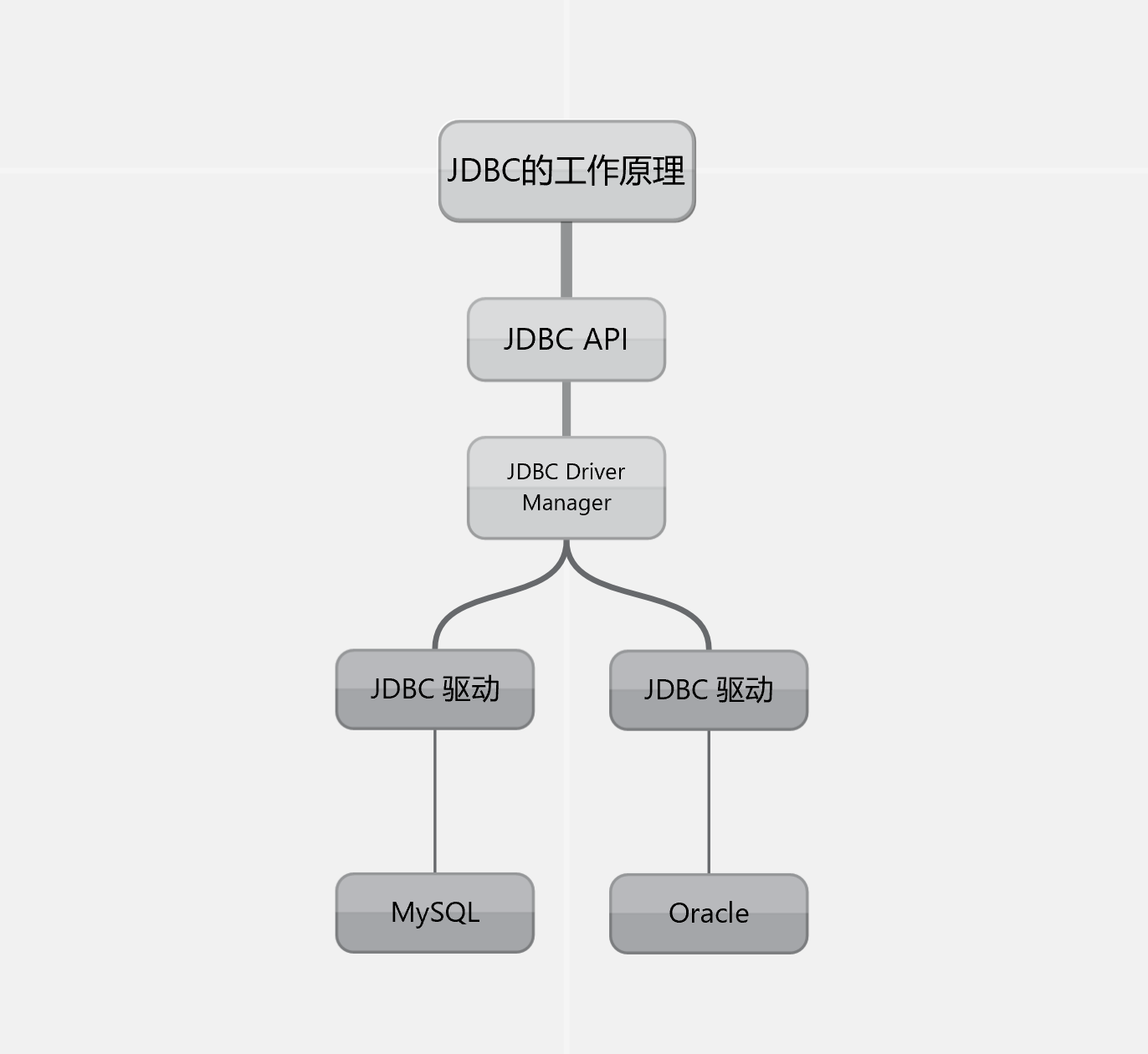
1. 架构
- JDBC 由 JDBC API & JDBC Driver Manager 主要组成
- JDBC API 主要提供给应用程序相关 数据库 相关 API,可用于:
- 加载 驱动程序
- 和数据库建立连接
- 执行 sql 语句
- JDBC Driver Manager 可选择对应的驱动程序来访问数据源,例如 MySQL,每个 JDBC Driver Manager 可支持连接到多个异构数据库的多个并发驱动程序
- 架构图如下:
2. 如何使用
Sting mysqlURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/flow0804?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true";
String username = "root";
String password = "123";
// 1. 装载 MySQL 驱动,只需要装载 一次
Class.forName ("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. Connection 与特定数据库的连接,在连接上下文中执行 sql 语句并返回结果
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection (mysqlURL, username, password);
// 3. 编写 sql 语句,并 创建执行 sql 语句的 statement
// 1) Statement 类
String id = "5";
String sql = "delete from table where id=" + id; // 有 SQL 注入风险
Statement st = conn.createStatement(); // 这里是 createStatement 函数
st.executeQuery(sql); // 执行简单 SQL 语句,不带参数
// 2) PreparedStatement 类
String sql = “select name, age from t_user where id = ? and sex = ?”;
PreparedStatement ps = conn.preparedStatement(sql); // 这里是 preparedStatement 函数
ps.setObject(1, "3"); // 占位符顺序从1开始
ps.setString(2, "女"); // 这里也可以使用 setObject
// 4. 处理执行结果
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
String sname = rs.getString("name");
String sage = rs.getString("age");
// doSomething()
}
// 5. 释放连接,使用完需要及时释放资源,因为比较耗资源,此外,还需要加 try...catch.. 约束
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close(); // 1) 关闭 ResultSet
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (st != null) {
st.close(); // 2) 关闭 PreparedStatement
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close(); 3) 关闭 Connection
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3. Statement 接口
1) Statement
- 通过
conn.createStatement()创建得到 - 用于发送简单的 SQL 语句,不带参数
- 有 SQL 注入 风险
public interface Statement extends Wrapper, AutoCloseable {
ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) throws SQLException;
int executeUpdate(String sql) throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
boolean execute(String sql) throws SQLException;
ResultSet getResultSet() throws SQLException;
//------------- JDBC 1.4 --------------
boolean execute(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException;
boolean execute(String sql, int columnIndexes[]) throws SQLException;
boolean execute(String sql, String columnNames[]) throws SQLException;
int executeUpdate(String sql, int columnIndexes[]) throws SQLException;
int executeUpdate(String sql, String columnNames[]) throws SQLException;
}
2) PreparedStatement
- 继承自 Statement 接口
- 通过
conn.prepareStatement(String sql)创建得到 - 可发送含有 参数 的 SQL 语句
- 执行效率高
- 可以防止 SQL 注入
- 预编译,编译 SQL 语句 & 执行 SQL 语句 这两个过程是分开的
- 当为其参数赋值值,只是将值传入,不需要再次经过编译,当批量处理时,该模板可以重复使用,只是里面的值不同而已,因此效率要高一些
- 通过
public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement {
// ----------- sql 执行 --------------
ResultSet executeQuery() throws SQLException; // sql 在 conn.preparedStatement(sql) 时已经预编译放入
int executeUpdate() throws SQLException;
boolean execute() throws SQLException;
// ----------- 参数设置,还有其他数据类型的设置方法 -----------------
void setString(int parameterIndex, String x) throws SQLException; // index 从 1 开始
void setObject(int parameterIndex, Object x, int targetSqlType)throws SQLException;
void setObject(int parameterIndex, Object x) throws SQLException;
}
3) CallableStatement
- 继承自
PreparedStatement接口 - 通过
conn.prepareCall(String sql)创建得到 - 用于调用 存储过程
public interface CallableStatement extends PreparedStatement {
void setString(String parameterName, String x) throws SQLException;
void setObject(String parameterName, Object x) throws SQLException;
String getString(String parameterName) throws SQLException;
Object getObject(String parameterName) throws SQLException;
}
4. 使用 JdbcTemplate
1) 如何使用
public class JDBCtemplate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
String sql="insert into user values (null,?)";
int i = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "吞佛");
System.out.println(1);
}
2) 源码
public class JdbcTemplate extends JdbcAccessor implements JdbcOperations {
// -------------------------- 构造函数 -----------------------
public JdbcTemplate() {
}
public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
this.setDataSource(dataSource);
this.afterPropertiesSet();
}
public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource, boolean lazyInit) {
this.setDataSource(dataSource);
this.setLazyInit(lazyInit);
this.afterPropertiesSet();
}
// -------------- 更新 ----------------
public int update(final String sql) throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(sql, "SQL must not be null");
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Executing SQL update [" + sql + "]");
}
class UpdateStatementCallback implements StatementCallback<Integer>, SqlProvider {
UpdateStatementCallback() {
}
public Integer doInStatement(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
int rows = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
if (JdbcTemplate.this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
JdbcTemplate.this.logger.trace("SQL update affected " + rows + " rows");
}
return rows;
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
}
return updateCount((Integer)this.execute(new UpdateStatementCallback(), true));
}
public int update(String sql, @Nullable Object... args) throws DataAccessException {
return this.update(sql, this.newArgPreparedStatementSetter(args));
}
// ---------------- 查找 ---------------------------
@Nullable
public <T> T query(final String sql, final ResultSetExtractor<T> rse) throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(sql, "SQL must not be null");
Assert.notNull(rse, "ResultSetExtractor must not be null");
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Executing SQL query [" + sql + "]");
}
class QueryStatementCallback implements StatementCallback<T>, SqlProvider {
QueryStatementCallback() {
}
@Nullable
public T doInStatement(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ResultSet rs = null;
Object var3;
try {
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
var3 = rse.extractData(rs);
} finally {
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(rs);
}
return var3;
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
}
return this.execute(new QueryStatementCallback(), true);
}
}